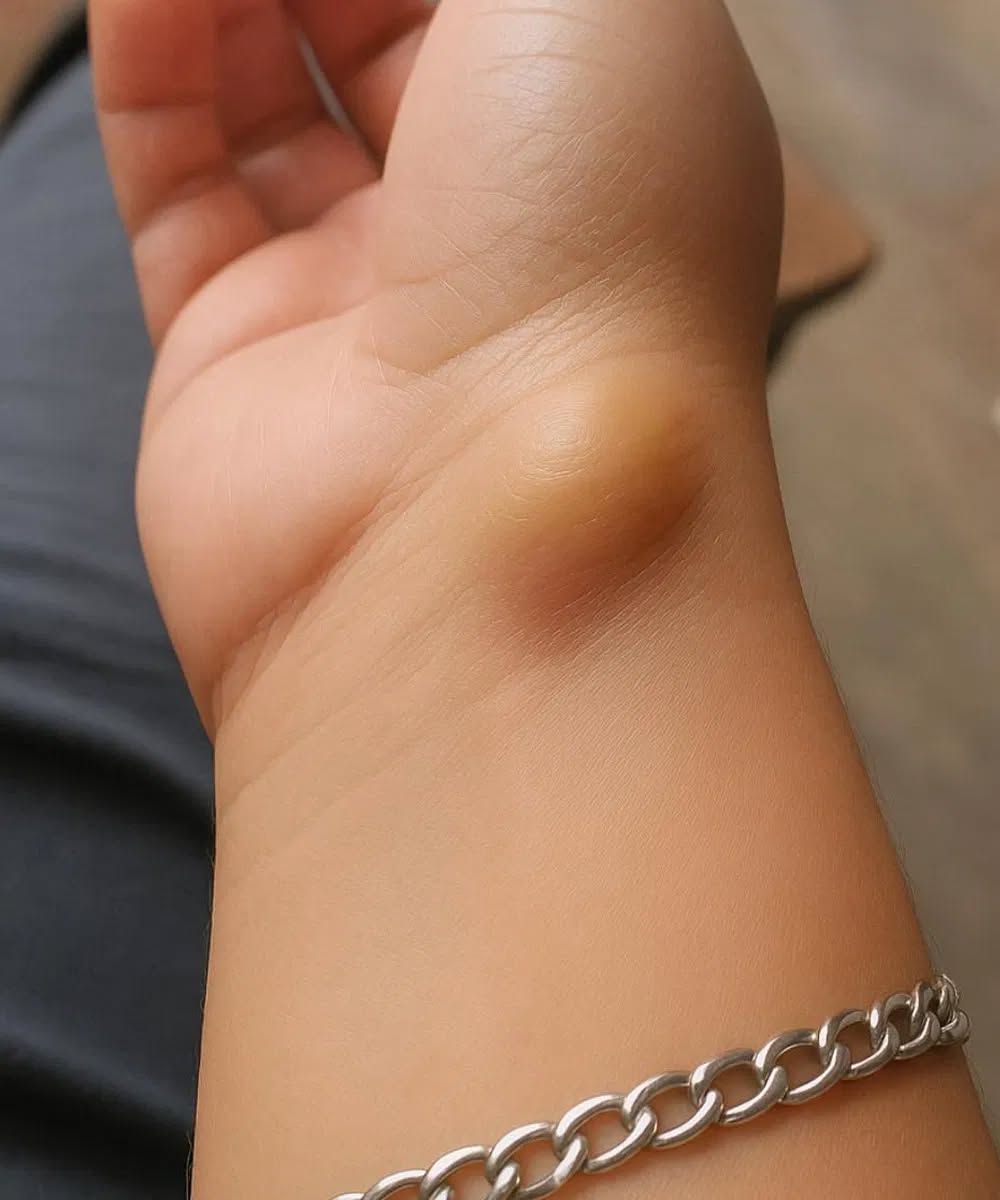
⚠️ Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

If you’ve noticed a strange lump, pay attention to these symptoms:
✅ Visible lump on the wrist, fingers, knees, or feet. It may be soft or firm to the touch.
✅ Progressive growth of the lump. In some cases, it appears and disappears over time.
✅ Pain or discomfort when moving the affected joint.
✅ Numbness, a feeling of pressure, or weakness in the area. This can occur if it presses on a nearby nerve.
✅ Changes in the skin. It may feel tighter or have a slight change in color.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, you should consult a specialist for a proper diagnosis.
📌 Why does this problem occur?
The causes can vary from person to person, yet certain factors that can trigger it include:
🔹 Repetitive movements. Activities that involve constant use of the wrists or fingers, such as typing, playing instruments, or certain sports.
🔹 Previous injuries to the joint. Blows or sprains can predispose to its development.
🔹 Arthritis or other joint conditions. Some diseases can cause synovial fluid buildup.
🔹 Genetic factors. If someone in your family has had this condition, you may be more likely to develop it.
🏥 When to see a doctor?
If the lump doesn’t cause discomfort and doesn’t affect movement, it may not require treatment and should simply be monitored. However, if you experience pain, discomfort, or limited movement, it’s best to see a specialist, such as an orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist.
🔬 Diagnostic methods
The specialist can make a diagnosis through:
🔹 Physical examination. They will touch the affected area to assess the lump’s size, texture, and tenderness.
🔹 Ultrasound or MRI. To look at the lump’s internal structure in more detail.
🔹 Fluid aspiration. In some cases, fluid is removed with a needle for analysis.
⚡ Treatment options
Treatment will depend on the severity of the case. Options include:
🔹 Observation. If there is no discomfort, the doctor may recommend monitoring.
🔹 Immobilization. Using a splint to reduce movement and decrease swelling.
🔹 Aspiration. The fluid is removed with a needle, although the lump may recur.
🔹 Surgery. If the lump is very large, painful, or keeps recurring, the doctor may suggest surgery to remove it.
🚨 Don’t try to pop it at home
Many people try to hit or press the lump to make it go away, but this can cause more harm than good. Manipulating it without medical supervision can cause inflammation, pain, or even infection.
🔎 Conclusion
If you’ve noticed a lump on your wrist or near a joint, pay attention to its symptoms and progress. Although in most cases it doesn’t represent a serious problem, if it causes discomfort or affects movement, it’s best to see a specialist for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
🔔 Don’t ignore your body’s signals. What seems like a simple thing can become a bigger problem if not treated promptly.